PIEZO DRIVE
Overview
Piezoelectric actuators require high-voltage, high-precision drive electronics capable of delivering fast, accurate, and stable voltage transitions into highly capacitive loads. Apex power operational amplifiers are widely used in piezo drive and deflection applications because of their linearity, high slew rates, fast settling times, and low crossover distortion.
Unlike traditional motor or inductive loads, piezo actuators rely on precise voltage control rather than continuous current delivery. Performance is largely determined by the amplifier’s ability to charge and discharge capacitance quickly and repeatably. Applications such as sonar transducer drivers, optical mirror positioning, and beam steering systems depend on rapid, random positioning with minimal overshoot or distortion.
Piezo drive systems often involve tradeoffs between voltage, speed, stability, and power dissipation. Selecting an appropriate analog device requires careful consideration of these factors to ensure consistent performance across operating conditions.
High Speed Power Operational Amplifiers
| Part | Slew Rate TYP [V/µs] | Supply Voltage MAX [V] | Output Current Cont. (Peak) [A] | Standby Current MAX [mA] | Power Dissipation MAX [W] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA107 | 3000 | 200 | 1.5 (5) | 56 | 62.5 |
| PA198 | 2000 | 450 | 0.2 | 25 | 30 |
| PA85 | 1000 | 450 | 0.2 | 25 | 30 |
| PA09 | 220 | 80 | 4.5 (5) | 85 | 78 |
High Voltage Power Operational Amplifiers
| Part | Supply Voltage MAX [V] | Output Current Cont. (Peak) [A] | Slew Rate TYP [V/µs] | Standby Current MAX [mA] | Power Dissipation MAX [W] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA99 | 2500 | 0.05 (0.07) | 30 | 4 | 37 |
| PA89 | 1200 | 0.075 (0.1) | 16 | 6 | 40 |
| PA94 | 900 | 0.1 (0.2) | 700 | 24 | 30 |
| PA97 | 900 | 0.01 (0.015) | 8 | 1 | 5 |
High Power Op Amps & PWM Amplifiers for Sonar Applications
| Part | Supply Voltage MAX [V] | Output Current Cont. (Peak) [A] | Slew Rate TYP [V/µs] | Standby Current MAX [mA] | Power Dissipation MAX [W] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA04 | 200 | 20 (20) | 50 | 90 | 200 |
| PA52 | 200 | 40 (80) | 50 | 36 | 400 |
| PA03 | 150 | 30 (30) | 8 | 300 | 500 |
| PA05 | 100 | 30 (30) | 100 | 120 | 250 |
| SA12 | 200 | 15 (20) | 250 |
Understanding Piezoelectric Actuators
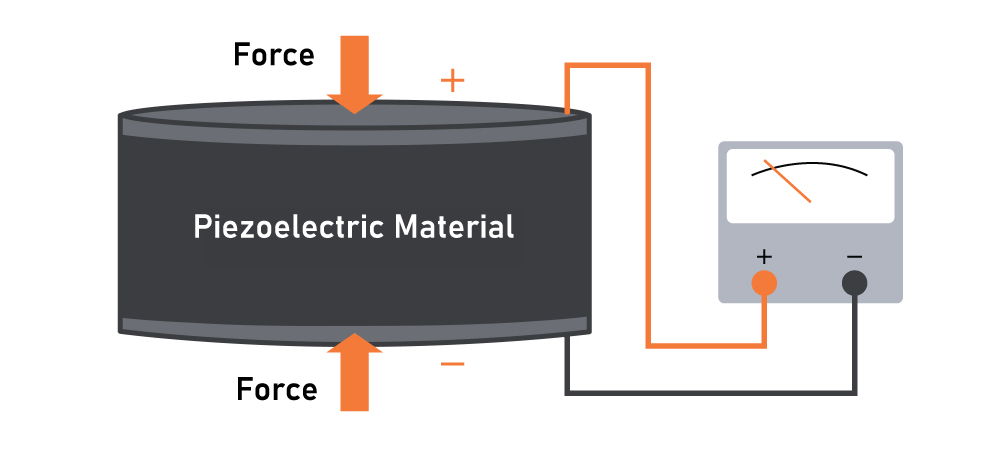
Piezoelectric actuators convert mechanical displacement into electrical energy through the piezoelectric effect, as shown above. When mechanical force is applied to a piezoelectric material, an electrical field is generated. Reversely, applying a voltage across the material causes it to expand or contract, producing controlled mechanical motion.
In actuator applications, piezoelectric elements behave primarily as capacitive loads, drawing current mainly during voltage transitions rather than at steady state. As a result, the drive electronics must supply both the required voltage range and sufficient dynamic current to achieve the desired displacement and response time.
Unlike inductive or resistive loads, piezo actuators offer extremely fast response times, high stiffness, and sub-micron to sub-nanometer positioning resolution. Their performance is strongly influenced by the quality of the voltage drive signal. Electrical noise, distortion, or limited slew rate translate directly into mechanical error, making the amplifier a critical element in determining system speed, stability, and positioning accuracy.
Common Requirements for Driving Piezoelectric Systems
Piezoelectric actuators impose a unique set of electrical requirements on the drive electronics. Because these devices behave primarily as capacitive loads and are often used in precision motion systems, the performance of the amplifier directly affects positioning accuracy, response time, and system stability.
Typical requirements for analog devices used to drive piezoelectric actuators include:
- High Output Voltage - Many piezo actuators require hundreds of volts to achieve full displacement. The amplifier must support the required voltage range with sufficient margin to maintain linear operation.
- High Slew Rate - Fast voltage transitions are necessary to achieve rapid actuation and high system bandwidth. Insufficient slew rate limits response time and reduces positioning performance.
- Peak Output Current Capability - Although piezo loads draw little to no current at steady state, significant peak current is required during voltage transitions to charge and discharge the actuator’s capacitance.
- Low Noise and Distortion - Electrical noise and signal distortion translate directly into mechanical error. Precision applications demand low output noise, minimal crossover distortion, and excellent linearity.
- Fast Settling Time and Stability - Overshoot, ringing, or instability caused by capacitive loading can degrade accuracy and repeatability. Amplifiers must remain stable while driving large capacitive loads.
- Thermal Performance and Power Dissipation - Reactive currents and high voltage operation can result in substantial internal power dissipation. Effective thermal management is critical to ensure reliable operation.
Apex Solutions
Apex power operational amplifiers are well suited for piezoelectric drive applications, combining high-voltage capability with the precision and dynamic performance required to control capacitive loads. Their fast slew rates, wide bandwidth, and low distortion enable accurate voltage control and rapid response, which directly translate to precise and repeatable actuator motion.
Designed for demanding operating conditions, Apex devices offer robust thermal performance and stable operation when driving large capacitances. For applications requiring higher output current or additional power bandwidth, Apex power boosters can be paired with precision amplifiers to extend performance while maintaining control accuracy and reliability.
- Sonar and Ultrasonic Transducer Drivers - High-voltage excitation of piezo transducers for acoustic transmission and sensing in underwater and nondestructive testing applications.
- Optical Mirror Positioning and Beam Steering - Fast, precise control of mirrors and optical elements in laser alignment, adaptive optics, and scanning systems.
- Precision Deflection and Positioning Systems - Nanopositioning stages, fine-motion actuators, and closed-loop positioning systems requiring sub-micron resolution.
- Medical and Diagnostic Imaging - Piezo drive electronics for ultrasound transducers and precision motion control in diagnostic and therapeutic equipment.
- Vibration Control - Piezo actuators used for structural vibration suppression, noise control, and dynamic stabilization.
- Semiconductor Equipment - High-accuracy motion and alignment in wafer inspection, lithography, and precision measurement systems.
- Industrial Printing Systems - High-speed, high-voltage piezo actuation for inkjet and material deposition systems used in industrial printing, additive manufacturing, and advanced packaging applications.
